What is Combinatorial
Chemistry?Combinatorial chemistry is a laboratory technique in which millions of molecular constructions can be synthesized and tested for biological activity. It has generated massive numbers of targeted molecules for testing and the developing techniques of high throughput screening has automated the screening process so larger numbers of biological assays can be done. All this together has reduced the discovery-to-market time from what used to be 10-14 years to 5-8 years.
In a traditional organic synthesis lab, the chemist does the standard reaction A + B --> C. But with combinatorial chemistry A is a mixture of perhaps 5 components and B is a mixture of 10 so instead of getting one product the chemist now gets 50. This collection of molecules synthesized so rapidly is referred to as libraries. The library allows for the input of a single generic structure, like benzodiazepine, with the output giving a complete range of benzodiazepine derivatives all in a specified molecular weight range which differ in the composition of the different R groups(figure 1). The output of which, as seen in figure 2, gives different derivatives of benzodiazepine. NETSCI Page .fig.1 fig.2
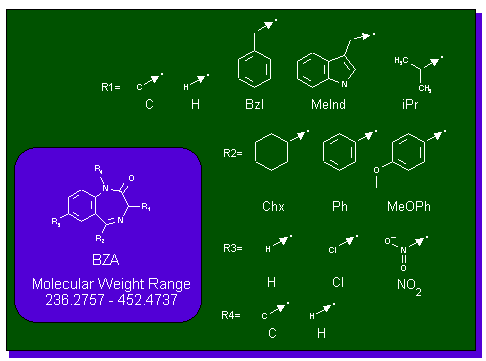
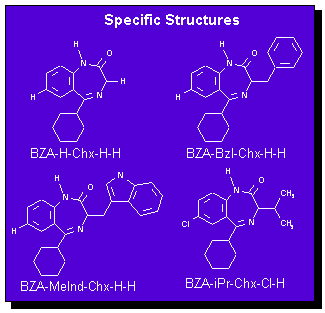
With its slight alterations around a general structure, combinatorial chemistry is an advanced way of finding a needle in a haystack. You can go fishing with a net the size of Delaware, but you’ll have a better chance of catching fish if you toss the net over the Atlantic than if you did over the Rockies. This merely stresses the importance of finding a general structure of biological importance and altering it to find activity, such as a better fit into an active site, rather than picking random molecules to synthesize. There are just too many possible structures and disastereomers of different classes of compounds to consider.
HomeWhat is Combinatorial Chemistry?
-- Solid Phase Synthesis
-- Future Applications of Combinatorial ChemistryMedicines Derived from Combinatorial Chemistry
The Value of The Rainforests
The Fate of the RainforestMedicines Discovered from rainforest Plants