|
Bigger Brains From MeatEveryone knows what meat does for us now but do people realize the significance that meat has had in human evolution. Eating meat is what has allowed humans to evolve to their current intellectual state. It all part of the meat cycle. Actually it's a process of increasing evolutionary advantage.  The concept is simple. Meat is an easily usable source of nutrition. So easy in fact that the digestive system does not need to be as large as that for gaining energy from non meat sources. This energy saved from not having to process less efficient materials (like vegetables) can go directly to the maintenance of other organs. In the human case the energy was used to increase the size of our brains, which allowed us to obtain more meat (Hence the nature of the cycle). The difference is striking. The figure below shows the expected and actual major organ sizes for humans based upon trends observed in higher primates. 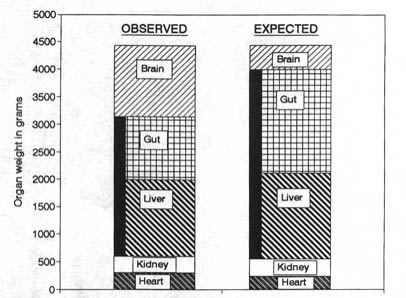 You can also see this in a graph of humans and some of our monkey friends. (We're number 7). 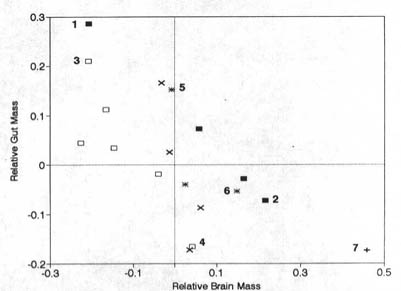 There is one last issue. It can be argued that all primates have large than expected brains, and that is true. The fact is that humans have much larger than expected brains. This discrepancy can be seen in the image below. 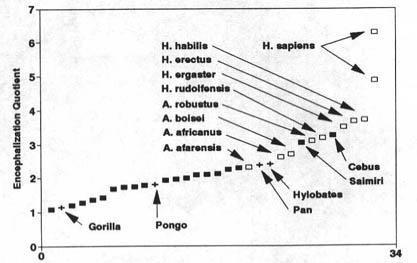 Encephalization quotient is basically the ratio of brain size to expected brain size. Humans are strikingly ahead of other primates. Since studies have shown that the only organs which diminished in size as our brains got large were our digestive tracts the conclusion is obvious. Eating meat allowed humans to have a source of energy efficient enough to allow our guts to shrink and our brains to grow. Only meat allows this to happen due to it's efficient delivery system. References
|
