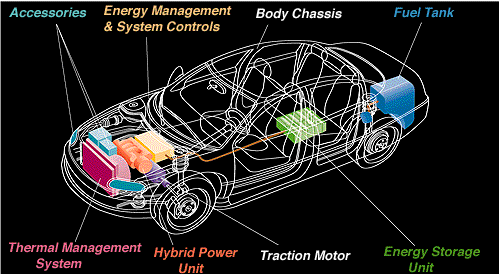
 |
| Energy conversion technologies - heat engines,fuel cells, electric generators or motors. | |
| Energy storage systems - fuel, batteries,ultracapacitors, or flywheels. | |
| Hybrid power unit - compression-ignition direct-injection (CIDI), spark-ignitiondirect-injection (SIDI), or gas turbine engines. |