Research Competitiveness Enhancement Model
The Bridging Advanced Developments for Exceptional Rehabilitation (BADER) Consortium approach was modeled after the National Institutes of Health Institutional Development Award – also known as IDeA – Networks of Biomedical Research Excellence, better known as the INBRE program.
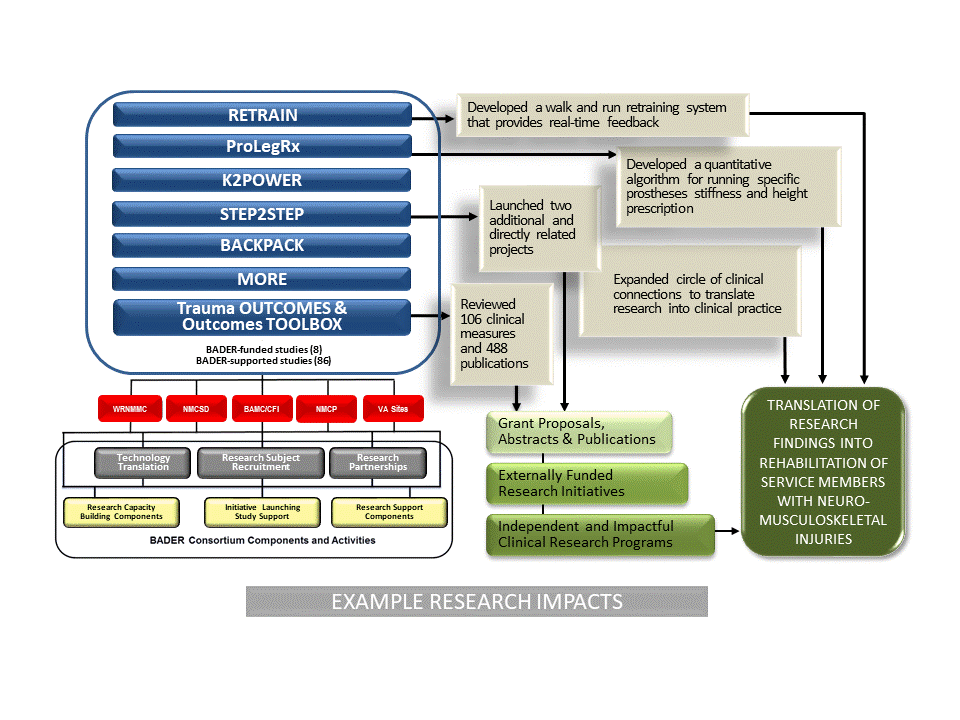 The Bridging Advanced Developments for Exceptional Rehabilitation (BADER) Consortium’s Research Competitiveness Enhancement Model was not simply a collection of research projects under one theme. It was a collection of strategically planned capacity-building and research support components combined with a dynamic, multidisciplinary network that enabled the entire consortium to lift up to maximize its ability to function administratively and to conduct research projects deemed impactful and important for the partner sites.The Consortium’s capacity-building components included:
The Bridging Advanced Developments for Exceptional Rehabilitation (BADER) Consortium’s Research Competitiveness Enhancement Model was not simply a collection of research projects under one theme. It was a collection of strategically planned capacity-building and research support components combined with a dynamic, multidisciplinary network that enabled the entire consortium to lift up to maximize its ability to function administratively and to conduct research projects deemed impactful and important for the partner sites.The Consortium’s capacity-building components included:
- A clinical research core
- Three scientific technical cores
- Expert affiliates
- Research advisory committees
- Education and training opportunities
Its research support components were:
- A master cooperative research and development agreement
- A centralized protocol and data management system
- An administrative core
Brought together the personnel and resources to ensure that the goals and scope of work of the BADER Consortium were achieved.
Developed and supported a research-intensive culture in four U.S. Department of Defense military treatment facilities (MTF) by assisting the MTFs with establishing a uniform and sustainable research infrastructure to facilitate ongoing and new MTF clinical research protocols across all sites.
Supported U.S. Department of Defense multi-site military treatment facility (MTF) clinical studies by providing additional scientific infrastructures and resources (Biostatistics, Outcomes Measurement and Biomechanics) for the conduct of clinical orthopaedic rehabilitation research.
