CREATE TABLE
Used
to
create the tables where data will be stored.
=========
Example:
1. Open the Orders table in design view.
2. Data type specified for each column:
Autonumber (Other
database systems: identity,
sequence)
Text
(char(n),
varchar(n))
Number
(In all database systems, various types depending on size
or type of number to be stored)
Date/Time
Currency
(money)
Additional data types not used in this table:
Memo
(long (Oracle, up to 2 GB text)
Yes/No
(boolean -not
available in some other database systems, e.g. Oracle)
OLE Object (blob, clob, raw)
Some additional data types in other database systems:
Timestamp
Interval
Enum
Set
3. Select each field and notice its properties
in the Field Properties grid, in particular:
Field (column) size
Caption (this is the column alias)
Required and
Allow Zero Length properties
Indexed
property
To view table structure and
column
properties in other databases:
describe
tablename
and
select [properties] from [system tables]
4. Close the Orders table.
The CREATE statement must specify the new table name, the column names, and the relevant data types and properties for each column.
Exercise:
Create a table to store personnel data, with a StaffID column as
primary
key
1. Type this SQL statement in the SQL query
design window:
CREATE TABLE Personnel (
StaffID text(9)
CONSTRAINT StaffPK PRIMARY KEY,
LastName text(15)
not null,
FirstName text(15)
not null,
Birthday date,
Department text(12)
null);
2. Execute the statement. If
Access reports syntax errors, find and
correct them.
3. Save the query as DefinePersonnel and close
it. In the database window, check the Query list for this DDL
query (notice that the icon for the query is different from the icon
for SELECT queries) and check the Table list for the new Personnel
table.
4. Run a query to select all records from the
new table:
SELECT * FROM Personnel;
The query returns one blank
record (in
other databases: 0 rows):
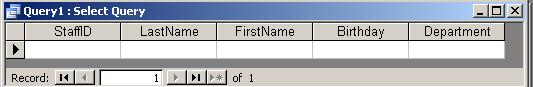
Close the query.
4. Open the new table in datasheet view – it is
empty and ready for data entry.
5. Change to design view and compare with the SQL statement. Also, choose View / Indexes and compare with the constraint created on StaffID:
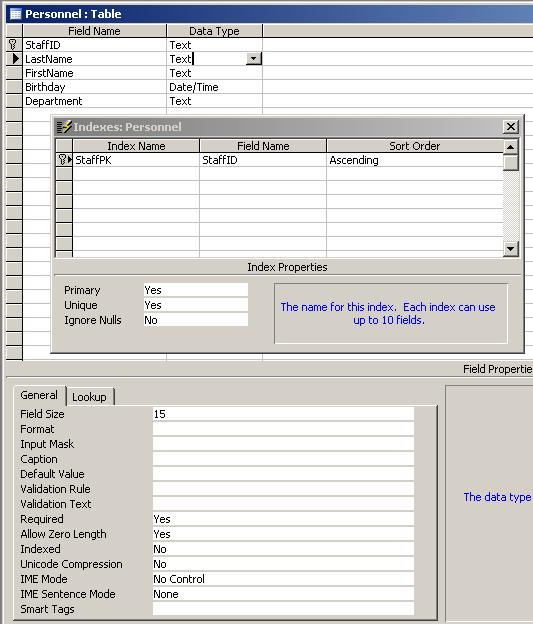
6. Close the Personnel table.