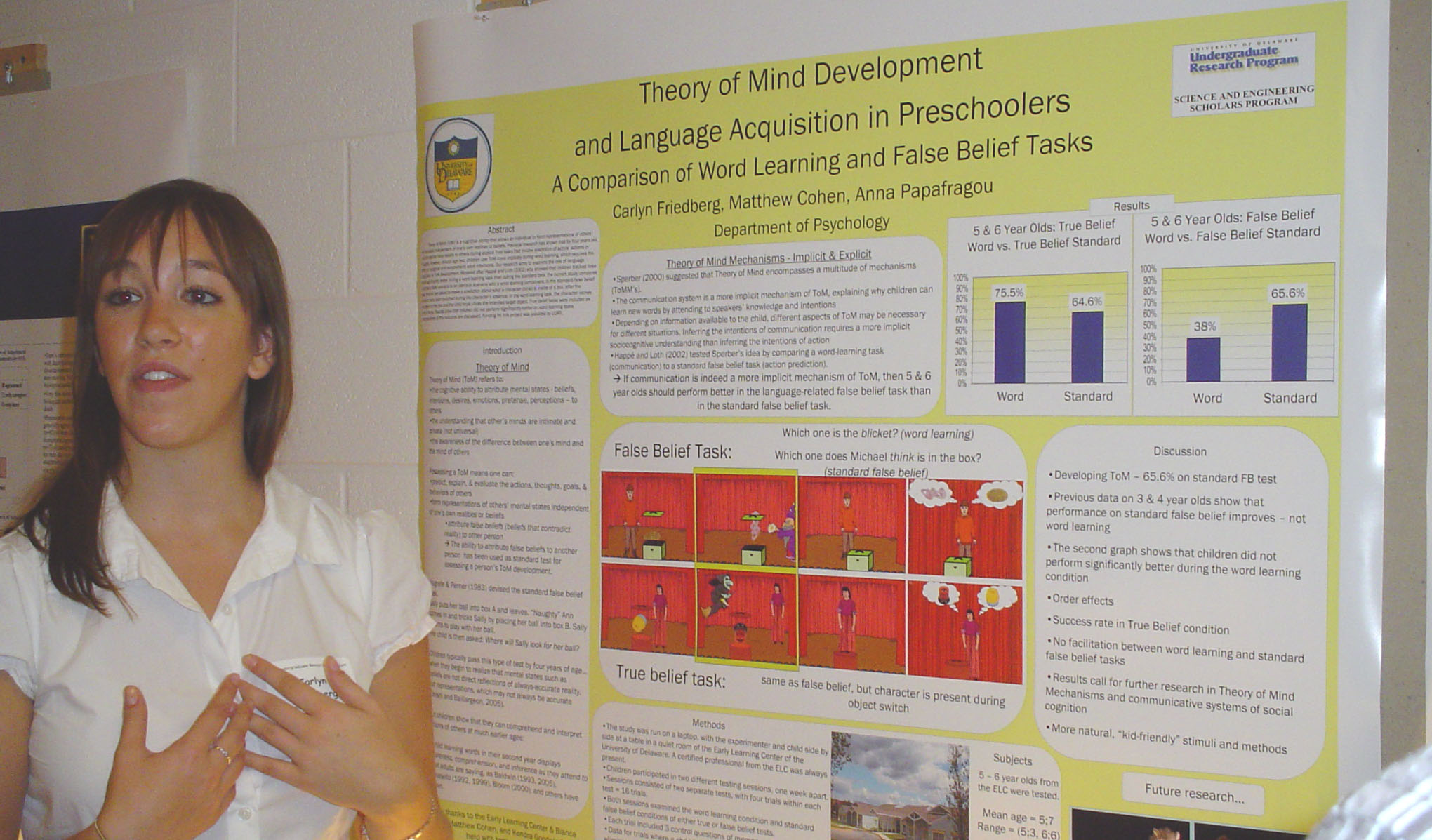
Theory of Mind Development and Language Acquisition in Preschoolers A Comparison of Word Learning and False Belief Tasks Carlyn Friedberg, Matthew Cohen, and Anna Papafragou Department of Psychology Theory of Mind (ToM) is a cognitive ability that allows an individual to form representations of others’ mental states independent of one’s own realities or beliefs. Previous research has shown that by four years old, children ascribe false beliefs to others during explicit ToM tasks that involve prediction of actors’ actions or thoughts. However, around age two, children use ToM more implicitly during word learning, which requires the ability to recognize and comprehend adult intentions. This project aims to examine the role of language acquisition in ToM development. Modeled after Happé and Loth (2002) who showed that children tracked false belief significantly better during a word learning task than during the standard task, the current study compares a standard false scenario to an identical scenario with a word learning component. In the standard false belief task, children are asked to make a prediction about what a character thinks is inside of a box, after the contents have been switched during the character’s absence. In the word learning task, the character names the object in the box and the child must chose the intended target object. True belief tasks were included as control items. Results show that children did not perform significantly better on word learning tasks. Interpretations of this outcome are discussed. |