Secure Shell (SSH) is a program that lets you log into your account on a computer connected to the Internet. Unlike a regular "Telnet" client, SSH establishes a secure connection between the computers by encrypting your password and other data.
- To connect to the University's main UNIX server, open the MacSSH PPC folder, and double-click the UDel icon.
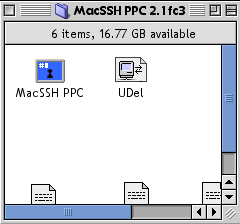
Note: If you wish to connect to a different server, double-click the MacSSH PPC icon and provide the name of the computer when prompted.
- In the Open Connection dialog box, select the computer with which you wish to connect. Copland ("copland.udel.edu" or "udel.edu") is the default computer with which you will establish a connection. You can use the triangle button to select two of the University's other central UNIX servers (Strauss or Mahler), or you may type the name of another computer that uses the Secure Shell protocol in the Host Name: box.

Click Connect.
- In the SSH2 login dialog box, provide your user name and password.
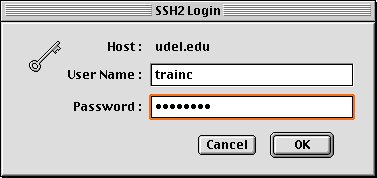
Click OK.
- The first time you establish an SSH connection to a specific computer, you must accept the remote computer's key fingerprint in order to have a secure connection.
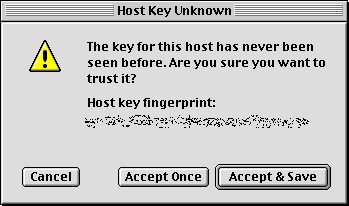
If you are connecting to one of the University's central servers, click Accept & Save. If you are making a one-time connection to another computer, click Accept Once.
- After your connection is established, you should see a text-based screen like the one below:
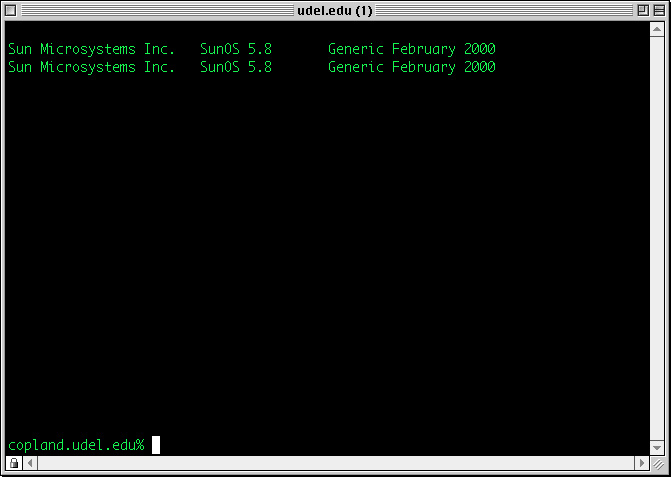
You can now work on the remote computer by typing UNIX commands and pressing the RETURN key after each command.
Since Secure Shell establishes a connection to a remote UNIX server, you can print files and e-mail messages on the University's central printers using standard UNIX commands. If, however, you wish to print e-mail messages or files using a local printer (e.g., one directly connected to your computer), follow these steps:
- If you are using Pine to read e-mail, use the Pine E (export) command to save the message to a file.
Exit or suspend the Pine program.
- Use the UNIX cat command to display the contents of the file you wish to print on your terminal screen. For example, if the file is named "katmessage", type this command at the UNIX prompt then press the RETURN key to display the file:
cat katmessage- If necessary, use the scrollbar to the right of the Secure Shell window to scroll backwards to the point in your session at which the beginning of the file is displayed.
- Highlight the entire display of the file you wish to print.
- With the text highlighted, select Print Selection from the File menu.
- Click Print to print the file or message.
To end your SSH session, follow these two steps:
- At the UNIX server's prompt, type exit as shown below:

Press the RETURN key. You are now logged out from the UNIX server.
- Quit the SSH program by pressing COMMAND-Q. (Press the COMMAND or Apple key and the Q key simultaneously.)
For further information about the University's central UNIX servers and about Pine and other UNIX programs, visit the IT Help Center's Web site (http://www.udel.edu/help).
Secure Shell main
page
Last updated July 27, 2002
Copyright © 2001 University of Delaware