EXAM 3 May 14, 1997 PHYS 208
Name:________________________________________________________
If you would like to change your grade-posting code, enter a 6-8
character code suitable for public display below; otherwise I will
continue to use your old code. If you wish, tell me not to post your
scores at all, whether or not you have previously given me a code to
use.
Code:_____________________
If you need a constant not given here or do not understand a
problem, please ask me about it.
No notes, books, etc. may be used during this exam.
| g = 9.8 m/sec2 |
Radius of the earth = 6.38 x 106 m |
Mass of the electron = 9.11 x 10-31 kg.
|
| e = 1.60 x 10-19 C |
mu0
---- = 1 x 10-7 Henry/m
4 pi
1
-------------- = 9.0 x 109 N m2/C2
4 pi epsilon0
|
|
For all problems, place the equations representing the physics
principles you are using in the box on the page. You may use the
general form of the equation or the form you get applying the
principle to the problem at hand. If no diagram is applicable to
a problem, write "none" in the diagram section.
1. (10 points)
(a) Give a good, quick way of remembering the
Biot-Savart law for the magnetic field due to a infinitesimal
segment of current.
(b). Name the magnetic-field equivalent of Gauss's Law
for electric fields and explain the analogies between the two.
2. (30 points, from homework)
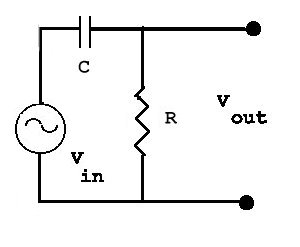
The circuit shown in the figure is called an RC high-pass filter
because high input frequencies are transmitted with greater amplitude
than low input frequencies. If the input voltage is
Vin = V0 cos(omega t),
find the amplitude of the output voltage.
Diagram:
Principles:
3. (30 points) A metal ring of area A is placed in a constant,
uniform field B in such a way that its area vector makes an angle
theta to the lines of B. The loop now rotates about a diameter so
that theta = omega*t. If the resistance of the coil is R, find the
current through the coil as a function of time.
Diagram:
Principles:
4. (30 points)
A very long, straight metal tube has inner radius a and
outer radius b . A current whose density is J = cr flows down
the tube. Find the magnetic field in the empty region inside
r = a and also within the metal, a < r < b .
Diagram:
Principles:
Use this page if necessary to continue any of the problems. Be sure to
label the problem number.
