SELF-JOIN
A
self-join
is a query in which a table is joined (compared) to itself. Self-joins are used to compare values in a
column with other values in the same
column in the same table. One practical use for
self-joins: obtaining running counts and running totals in an SQL
query.
To
write
the query, select from the same table listed twice with different
aliases, set
up the comparison, and eliminate cases where a particular value would
be equal to
itself.
Example
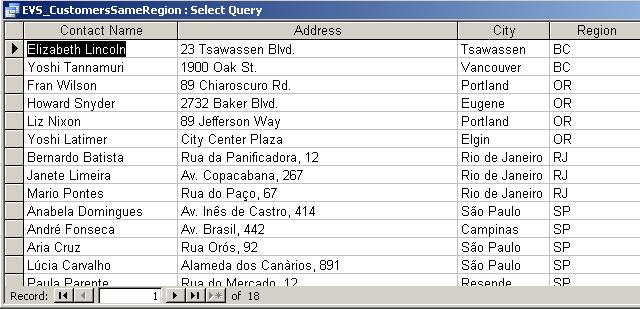
Which
customers are located in the same state (column name is Region)?
Type this statement in the SQL window:
SELECT DISTINCT c1.ContactName,
c1.Address, c1.City, c1.Region
FROM Customers AS c1, Customers AS
c2
WHERE c1.Region = c2.Region
AND c1.ContactName <>
c2.ContactName
ORDER BY c1.Region, c1.ContactName;
The result
should look like this:
Exercise
Which
customers are located in the same city? (32 rows)