For practice using SQL
commands in
MS Access:
Unless
otherwise indicated:
–
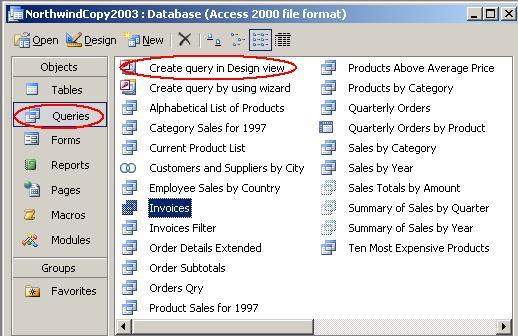
In the database window,
under
Objects, select Queries and double-click on "Create query in Design
view" (both circled below):
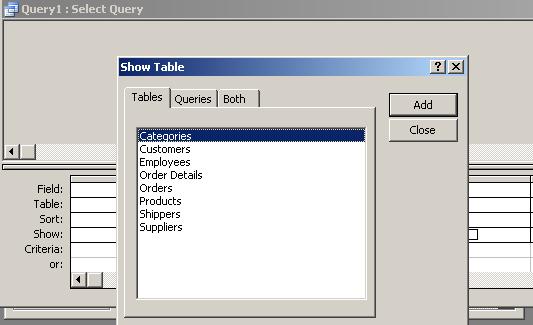
–
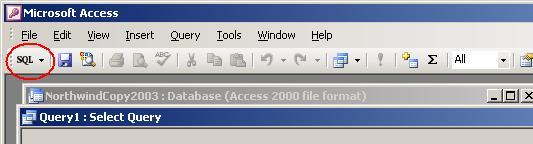
Close
the Show Table dialogue box and click the SQL view button (circled) or
choose View / SQL View from the menu bar:
–
In
the window called "Query1: Select Query", type the SQL statement,
replacing SELECT with the appropriate
SQL
command. Be
sure to
keep the semi-colon statement terminator:
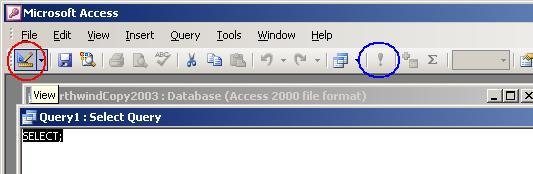
–
To
execute the command, click the Run button (!) or choose Query / Run
from
the menu bar or use the View button (see note). Both buttons are
circled in the figure above. (Note: In MS Access, but not in other relational database
systems, the View button allows you to see which records or how
many records will be changed by queries that modify data, without
actually
executing the query.)
–
Save
the query (File / Save or click the Save button next to the View
button) and close the SQL design window. You may reuse the window for
other queries (one query at a time) and save each query with a
different name using File / Save As... from the menu
bar. Caution: If you reuse the SQL window and click the
Save button, you will overwrite your original query.
===============================================================================
MS
Access
denotes all DML statements except SELECT queries as "action queries"
and warns the user any
time data will be modified.
Here is the list of steps for DML
exercises:
1.
Type the statement in the SQL window.
2.
Check results without executing by switching to Datasheet view.
3.
Execute the statement (click Yes
when prompted
about continuing).
4.
Check the results in the appropriate table.
5.
Save the statement and close it.
Access may change the SQL
in non-standard
ways when you leave the SQL window.
This does not change how the
statement works.
==============================================================================