There are 9 pages to this examination. Put your name on each new page. The pages in the back display all of the metabolic pathways we have discussed in class. You may tear them off and refer to them. A genetic code chart is at the bottom of page 5. If you feel any question is unclear or ambiguous, clearly explain your answer or interpretation.
Do not expose your answers to the scrutiny of your neighbors. Please fold under each page before you go on to the next.
Breakdown of the exam by sections:
Structures
14 Points
Short Answer
20 Points
Multiple Choice
21 Points
Problems and Short Essay 45 Points
Total
100 Points
(Possible Bonus
12 Points)
Class Average = 55.44
Range 19 - 99
N = 50
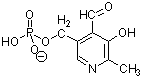
1. (8 Points) Draw the structure of the deoxyribodinucleotide
represented by pAT.
2. ( 6 Points) Identify the following molecules and indicate
their respective functions.
 |
a. ________________________ b. _______________________ c. ______________________
Function
___________________________ ________________________ ________________________
___________________________ ________________________ ________________________
Short Answer (20 points, 1 point each)
________________ 1. Number of subunits in aspartate transcarbamoylase.
________________ 2. Form in which carbon for fatty acid synthesis is exported from the mitochondrion.
________________ 3. Human sex-linked disease associated with purine salvage.
________________ 4. A pathway that generates NADPH for reductive biosynthesis.
________________ 5. A photochemical product of UV irridation of DNA.
________________ 6. In humans during sleep, this organ consumes almost 50% of the oxygen inspired.
________________ 7. Trinucleotide sequence common to the 3' end of all tRNAs.
________________ 8. Chemical name for the bond that links an amino acid to its cognate tRNA.
________________ 9. Form in which birds excrete nitrogen.
________________ 10. Normally the exclusive energy source for brain metabolism.
________________ 11. Naturally occurring single-strand pieces of DNA that extend an RNA primer.
________________ 12. Way in which ethidium bromide binds to DNA.
________________ 13. During prolonged starvation, the primary energy source for humans is.
________________ 14. Increase in A260 absorbance of DNA when heated.
________________ 15. Kwashiorkor is a disease of humans due to a deficiency of what in the diet?
________________ 16. Antibiotic analog of p-aminobenzoate (PABA).
________________ 17. Portion of eukaryotic mRNA that doesn't hybridize with genomic DNA.
________________ 18. Noncoding segments of DNA within eukaryotic genes.
________________ 19. Major protein component of nucleosomes.
________________ 20. Inhibitor of purine and pyrimidine metabolism used in cancer chemotherapy.
Bonus (3 Points). Who was Daniel Nathans and what did he do?
____ 1. In a short term experiment, an 15N-labeled amino group from glutamic acid gets distributed widely among other amino acids including arginine in which 3 of the 4 nitrogens become labeled. Which of the identified nitrogens of arginine would not be labeled quickly?
____ Bonus (1 Point) True or False, 15N is
a radioactive isotope.
____ 2. If a random RNA polymer containing equal molar
amounts of A, U, and C were used as an artificial mRNA in a complete translation
reaction under conditions of random initiation, Which amino acid would
not be expected in the polypeptide product?
A. Methionine
B. Lysine C. Phenylalanine
D. Serine E. Leucine
____3. Protein synthesis and fatty acid synthesis are both biological polymerization processes and have analogous steps. Consider the following pairs of components and identify the pair that does not correspond.
A. Fatty Acid Synthetase Ribosome
B. Acetyl CoA fMet tRNA
C. Malonyl CoA aminoacyl tRNA
D. NADPH ATP
E. palmitoyl-Enz
peptidyl-tRNA
____ 4. Which of the following is not associated with transcription?
A. ATP
B. RNA polymerase C. CTP
D. TTP E. DNA
____ 5. The Cori Cycle is a cooperative venture between
skeletal muscles and the liver, with the blood stream as the means of communication
between these tissues. Select the statement that is FALSE about the Cori
Cycle.
A. It operates primarily when muscle is actively working.B. In muscle, glycolysis is occurring, while in liver gluconeogenesis is occurring.
C. Lactate dehydrogenase operates in the direction pyruvate to lactate in muscle, whereas in liver it operates in the direction lactate to pyruvate.
D. The blood transports glucose from muscle to liver and then transports lactate from the liver back to muscles.
E. The Cori Cycle operates at the expense of ATP in liver
____ 6. A synthetic repeating RNA used as a messenger
in an in vitro protein synthesis system produces an alternating polypeptide
containing a basic amino acid and an acidic amino acid. What is the sequence
of the synthetic mRNA?
A. (GAA)n
B. (AAG)n C.
(AG)n D. (CG)n
E. (CGC)n
____ 7. In comparing proteins among individuals of the same species, researchers commonly find variants due to a single amino acid replacement. These allelic variations are usually due to single base substitution mutations. If one observed an arginine in place of a serine in a particular pair of allelic proteins, which one of the following amino acids would be LEAST likely to be found at the same position in another variant of the same protein.
A. Cysteine B. Isoleucine C. Asparagine D. Tyrosine E. Valine
Genetic Code Table
| UUU |
PHE |
UCU |
SER |
UAU |
TYR |
UGU |
CYS |
| UUC | UCC | UAC | UGC | ||||
| UUA | LEU | UCA | UAA |
End |
UGA | End | |
| UUG | UCG | UAG | UGG | TRP | |||
| CUU | CCU |
PRO |
CAU | HIS | CGU |
ARG |
|
| CUC | CCC | CAC | CGC | ||||
| CUA | CCA | CAA |
GLN |
CGA | |||
| CUG | CCG | CAG | CGG | ||||
| AUU |
ILE |
ACU |
THR |
AAU |
ASN |
AGU |
SER |
| AUC | ACC | AAC | AGC | ||||
| AUA | ACA | AAA | LYS | AGA |
ARG |
||
| AUG | MET | ACG | AAG | AGG | |||
| GUU |
VAL |
GCU |
ALA |
GAU |
ASP |
GGU |
GLY |
| GUC | GCC | GAC | GGC | ||||
| GUA | GCA | GAA |
GLU |
GGA | |||
| GUG | GCG | GAG | GGG |
1. (8 Points) While some athletes consume creatine to
enhance performance, our bodies are perfectly capable of synthesizing creatine
from compounds you know. From the two step pathway outlined below, provide
the names of the precursors (A and B) whose structures are given and predict
the structure of the intermediate (C) and byproduct (D) in the pathway.
What would be the fate of D?
2. (6 Points) A number of years ago, the diagram below appeared on a seminar announcement from the Delaware Chapter of the American Chemical Society. The artist did not get good advice from the chemists. How does this representation differ significantly from the Watson and Crick model for DNA?
3. To determine the essential amino acids for the mouse,
Steele (1952) fed a mouse 14C-glucose. Three days later he hydrolyzed
protein from the mouse and measured the radioactivity in each of the separated
amino acids. His recovery of 14C (nanoCuries/mg Carbon) in different
amino acids is shown below.
| Amino
Acid |
nCi/mgC |
Amino
Acid |
nCi/mgC |
Amino
Acid |
nCi/mgC |
Amino
Acid |
nCi/mgC |
|||
| Alanine | 26.5 ± 3.3 | Glutamate | 19.0 ± 1.9 | Lysine | 0.0 ± 0.02 | Serine | 8.4 ± 0.1 | |||
| Arginine | 3.0 ± 0.2 | Glycine | 5.1 ± 0.2 | Methionine | 1.03 ± 0.06 | Threonine | 0.09 ± 0.02 | |||
| Aspartate | 15.8 ± 0.9 | Histidine | 0.07 ± 0.08 | Phenylalanine | 0.02 ± 0.07 | Tyrosine | 0.0 ± 0.07 | |||
| Cysteine | 3.3 ± 0.3 | Isoleucine | 0.06 ± 0.05 | Proline | 3.1 ± 0.1 | Valine | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
Your textbook lists histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, threonine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and valine as essential amino acids for mammals.
A. (4 Points) Provide a clear explanation for why alanine, aspartate, and glutamate are so highly labeled compared to the other amino acids.
B. (4 Points) Would you consider adding or removing any amino acids from the list of essential amino acids based on the Steele's results? Explain.
4. A. (4 Points) In order to determine the specificity of a new Type II restriction endonuclease, BioI, a circular 30,000 base-pair, double-stranded DNA was cleaved and its nucleotide sequence determined at both 5' ends of each restriction fragment. The consensus sequence was pTATCNNN... where N can be any deoxyribonucleotide. What hexanucleotide sequence does BioI recognize?
B. (6 Points) If the circular DNA used above contained 30% G and its nucleotide sequence were assumed to be random, how many BioI restriction sites would you expect in the entire sequence? Show your work and describe your thinking.
5. (7 Points) The diagram below is an idealized representation of the combined processes of transcription and translation as it has been observed by electron microscopy in lysed E. coli cells. Label the diagram clearly indicating the (1) DNA strand, (2) RNA Polymerase and (3) its direction of movement relative to DNA, (4) mRNA and (5) its 3' to 5' orientation, (6) a ribosome and (7) its direction of movement, and (8) the location of the promoter for the gene. Finally, put an "X" on the ribosome that would have the longest incomplete protein attached to it.
Bonus (2 Points) Why would this never be seen in a eukaryotic
cell?
6. (6 Points) Essay. Describe how the human body adapts
metabolically to starvation.
7. Bonus Question (6 Points) In 1995, Berthold et al.
(Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 92, 10123) published a study to determine
availability of dietary purines and pyrimidines for the chicken and mouse.
They grew algae in the presence of 13CO2 and then
isolated 13C-containing RNA from them which they fed to a hen
for 4 weeks and to four mice for 6 days. They then isolated hepatic RNA
and measured the 13C-enrichment of the nucleotide bases by mass
spectrometry. The % 13C derived from the diet for each nucleoside
for both animals is indicated in the table below. How would you interpret
these data?
| Animal | Adenosine | Guanosine | Cytidine | Uridine |
| Chicken | 2.9 | 2.0 | 84.6 | 86.6 |
| Mouse | 3.6 | 3.6 | 22.8 | 27.4 |