 The Chemistry of Caffeine
The Chemistry of Caffeine 
 The Chemistry of Caffeine
The Chemistry of Caffeine 
I WHAT IS CAFFEINE:
Caffeine Synonyms: 1-methyltheobromine
Figure
CH3
|
N
/ \
N----C C==O
|| || |
|| || |
CH C N--CH3
\ / \ /
N C
| ||
CH3 O
Also see
www.geocities.com/CapeCanaveral/Launchpad/6202/che.htm
Physical Properties:
Molecular Formula = C8H10N4O2
Molecular Weight =
194.19
Number of Chiral Centers:
Zero
Optical Activity:
None
UV max (10mM HClO4
+
10mM NaClO4 70%) + (CH3CN 30%): 210nm, local max
at 275nm
Half-Life: in human
body varies between 3 to 7 hours
Properties: Soft,
white crystal or powder, odorless, slightly bitter taste
Melting Point: 235-238oC
Caffeine is classified
as a central nervous system stimulant and it belongs to xanthine chemical
group. There are three distinguished compounds in xanthine group:
Caffeine: 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine
Sources: Coffee, tea, cola nuts, mate, guarana
Effects: Stimulant of central nervous system, cardiac muscle, and respiratory
system, diuretic Delays fatigue
Theophylline: 1,3-dimethylxanthine
Sources: Tea
Effects: Cardiac stimulant, smooth muscle relaxant, diuretic, vasodilator
Theobromine: 3,7-dimethylxanthine
Sources: Principle alkaloid of the cocoa bean, Cola nuts, and tea
Effects: Diuretic, smooth muscle relaxant, cardiac stimulant, vasodilator
They are very similar and differ only by the presence of methyl groups in two positions of the chemical structure. They are easily oxidized to uric acid and other methyluric acids, which are also similar in chemical structure.
II SOURCES OF CAFFEINE:
Drinks:
| Item | Item Size | Caffeine Content (mg) |
| Tea | 150 ml | 2-5 |
| Hot Cocoa | 150 ml | 1-8 |
| Chocolate Milk | 225 ml | 2-7 |
| Jolt Cola | 12 oz | 71 |
| Josta | 12 oz | 58 |
| Mountain Dew | 12 oz | 54 |
| Kick Citrus | 12 oz | 54 |
| Mello Yellow | 12 oz | 53 |
| Surge | 12 oz | 51 |
| Tab | 12 oz | 47 |
| Diet Coca Cola | 12 oz | 46 |
| Coca Cola | 12 oz | 46 |
| Dr. Pepper | 12 oz | 41 |
| Mr. Pibb | 12 oz | 40 |
| Pepsi Cola | 12 oz | 38 |
| Aspen | 12 oz | 36 |
| Canada Dry Cola | 12 oz | 30 |
| RC Cola | 12 oz | 18 |
| Mug Root Beer | 12 oz | 0 |
| Sprite | 12 oz | 0 |
| 7-Up | 12 oz | 0 |
Coffee:
| Item | Item Size | Caffeine Content (mg) |
| Coffee, Brewed | 8 oz | 135 |
| General Foods International Coffee, Orange Cappuccino | 8 oz | 102 |
| Coffee, instant | 8 oz | 95 |
| General Foods International
Coffee, Café Vienna |
8 oz | 90 |
| Maxwell House Cappuccino, Mocha | 8 oz | 60-65 |
| General Foods International Coffee, Swiss Mocha | 8 oz | 55 |
| Maxwell House Cappuccino, French Vanilla or Irish Cream | 8 oz | 45-50 |
| Maxwell House cappuccino, Amaretto | 8 oz | 25-30 |
| General Foods International Coffee, Viennese Chocolate Café | 8 oz | 26 |
| Maxwell House Cappuccino, Decaffeinated | 8 oz | 3-6 |
| Coffee, Decaffeinated | 8 oz | 5 |
Food:
| Item | Item Size | Caffeine Content (mg) |
| Ben/Jerry No Fat Coffee Fudge Froz. Yog. | 1 cup | 85 |
| Starbucks Coffee Ice Cream | 1 cup | 40-60 |
| Dannon Coffee Yogurt | 8 oz. | 45 |
| Chocolate Bar | 50 g | 3-63 |
| Chunky Bar | 1 bar (40g) | 11.6 |
| 100 Grand Bar | 1 bar (43g) | 11.2 |
| Nestle Crunch Bar | 1 bar (40g) | 10 |
| Krackel Bar | 1 bar (47g) | 8.5 |
| Peanut Butter Cup | 1 pk (51g) | 5.6 |
| Kit Kat Bar | 1 bar (46g) | 5 |
| Mr. Goodbar | 1 bar (50g) | 5 |
| Raisinets | 10 pieces (10g) | 2.5 |
| Butterfinger Bar | 1 bar (61g) | 2.4 |
| Baby Ruth Bar | 1 bar (60g) | 2.4 |
| Special Dark Sweet Chocolate Bar | 1 bar (41g) | 31 |
| Chocolate Brownie | 1.25 oz | 8 |
| Chocolate Chip Cookie | 30 g | 3-5 |
| Chocolate Ice Cream | 50 g | 2-5 |
| Milk Chocolate | 1 oz | 1-15 |
| Bittersweet Chocolate | 1 oz | 5-35 |
| After Eight Mint | 2 pc (8g) | 1.6 |
| Jell-O Pudding Pop Chocolate | 1 bar (77g) | 2 |
| Jell-O Mix Chocolate Mousse | 95 g | 6 |
| Jell-O Chocolate Fudge Mousse | 86 g | 12 |
Non-prescription Drugs:
| Item (1 tablet or capsule) | Caffeine Content (mg) |
| Dextrim | 200 |
| Vivarin | 200 |
| No Doz | 100 |
| Excedrin | 65 |
| Vanquish | 33 |
| Anacin | 32 |
| Midol | 32 |
| Triaminicin | 30 |
| Dristan | 16 |
III HOW CAFFEINE WORKS:
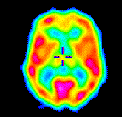
To a nerve cell, caffeine looks like adenosine that causes drowsiness by slowing down nerve cell activity. Caffeine therefore binds to the adenosine receptor. However, it does not slow down the cell/s activity like adenosine would. So the cell cannot see adenosine anymore because caffeine is taking up all the receptors adenosine binds to. Therefore instead of slowing down because of the adenosine level, the cells speed up. You can see that caffeine also causes the brain’s blood vessels to constrict, because it blocks adenosine’s ability to open them up.
IV OVERDOSE:
The lethal dosage varies from individual to individual
according to weight. In massive doses, caffeine is lethal. A fatal dose
of caffeine has been calculated to be more than 10 grams, about 80 to 100
cups of coffee in rapid succession.
Home
- Chemistry - Physiological
Effect
Psychological
Effect - Conclusion
Other
links - Contact